Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Aoki, So; Kondo, Keietsu; Yamamoto, Masahiro
no journal, ,
The influence of long term thermal aging (LTA) on SCC initiation susceptibility in L-grade austenitic stainless steels (SSs) has been investigated using Creviced Bent Beam (CBB) tests. Test materials were type 304L and 316L SSs, and aging heat treatments were conducted at 288 C in air for up to 14000 hours followed by solution-annealing (SA) or 20% cold-working (CW). The evaluation of the SCC initiation susceptibility was conducted by CBB tests in BWR simulated high-temperature water at 288
C in air for up to 14000 hours followed by solution-annealing (SA) or 20% cold-working (CW). The evaluation of the SCC initiation susceptibility was conducted by CBB tests in BWR simulated high-temperature water at 288 C for 1000 hours. It was revealed by CBB tests that 304L-SA, 304L-CW, 304L-SA+LTA, 304L-CW+LTA, 316L-SA 316L-CW and 316L-SA+LTA showed no SCC initiation susceptibility, whereas 316L-CW+LTA showed high SCC susceptibility. To clarify the cause of SCC initiation in 316L-CW+LTA, several investigations are in progress from the viewpoint of mechanical properties, cold-rolling texture, microstructure and michrochemistry after LTA. It is considered that the low temperature sensitization was not the main cause of SCC in 316L-CW+LTA, because the TEM/EDX analysis on the 316L+LTA and 316L-CW+LTA specimens showed no chromium depletion in the vicinity of grain boundaries. In this presentation, we will explain the further investigation results for effect of LTA on SCC initiation susceptibility in L-grade austenitic SSs.
C for 1000 hours. It was revealed by CBB tests that 304L-SA, 304L-CW, 304L-SA+LTA, 304L-CW+LTA, 316L-SA 316L-CW and 316L-SA+LTA showed no SCC initiation susceptibility, whereas 316L-CW+LTA showed high SCC susceptibility. To clarify the cause of SCC initiation in 316L-CW+LTA, several investigations are in progress from the viewpoint of mechanical properties, cold-rolling texture, microstructure and michrochemistry after LTA. It is considered that the low temperature sensitization was not the main cause of SCC in 316L-CW+LTA, because the TEM/EDX analysis on the 316L+LTA and 316L-CW+LTA specimens showed no chromium depletion in the vicinity of grain boundaries. In this presentation, we will explain the further investigation results for effect of LTA on SCC initiation susceptibility in L-grade austenitic SSs.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Seto, Hitoshi*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth tests using compact tension (CT) specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) were performed in simulated BWR environments (at  288
288 C). Moreover, microstructures of deformed areas were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM) after straining tensile specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L SSs. As a result, for lower neutron dose than
C). Moreover, microstructures of deformed areas were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM) after straining tensile specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L SSs. As a result, for lower neutron dose than 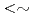 1.9 dpa, the crack growth rates (CGRs) show effective environmental mitigation and the deformed structures show tangling of dislocations. On the other hand, for higher neutron dose than
1.9 dpa, the crack growth rates (CGRs) show effective environmental mitigation and the deformed structures show tangling of dislocations. On the other hand, for higher neutron dose than 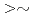 2.7 dpa, the CGRs show small environmental mitigation and the deformed structures consist mainly of dislocation channels. From the relationship between CGRs and deformed structures, mechanisms on IASCC growth will be discussed.
2.7 dpa, the CGRs show small environmental mitigation and the deformed structures consist mainly of dislocation channels. From the relationship between CGRs and deformed structures, mechanisms on IASCC growth will be discussed.